Z.H. Bi, A.P. Zhang, G.R. Wang, C. Dong, X.Y. Shi and Z.-S. Wu *
Science Bulletin, 2024, Accepted.
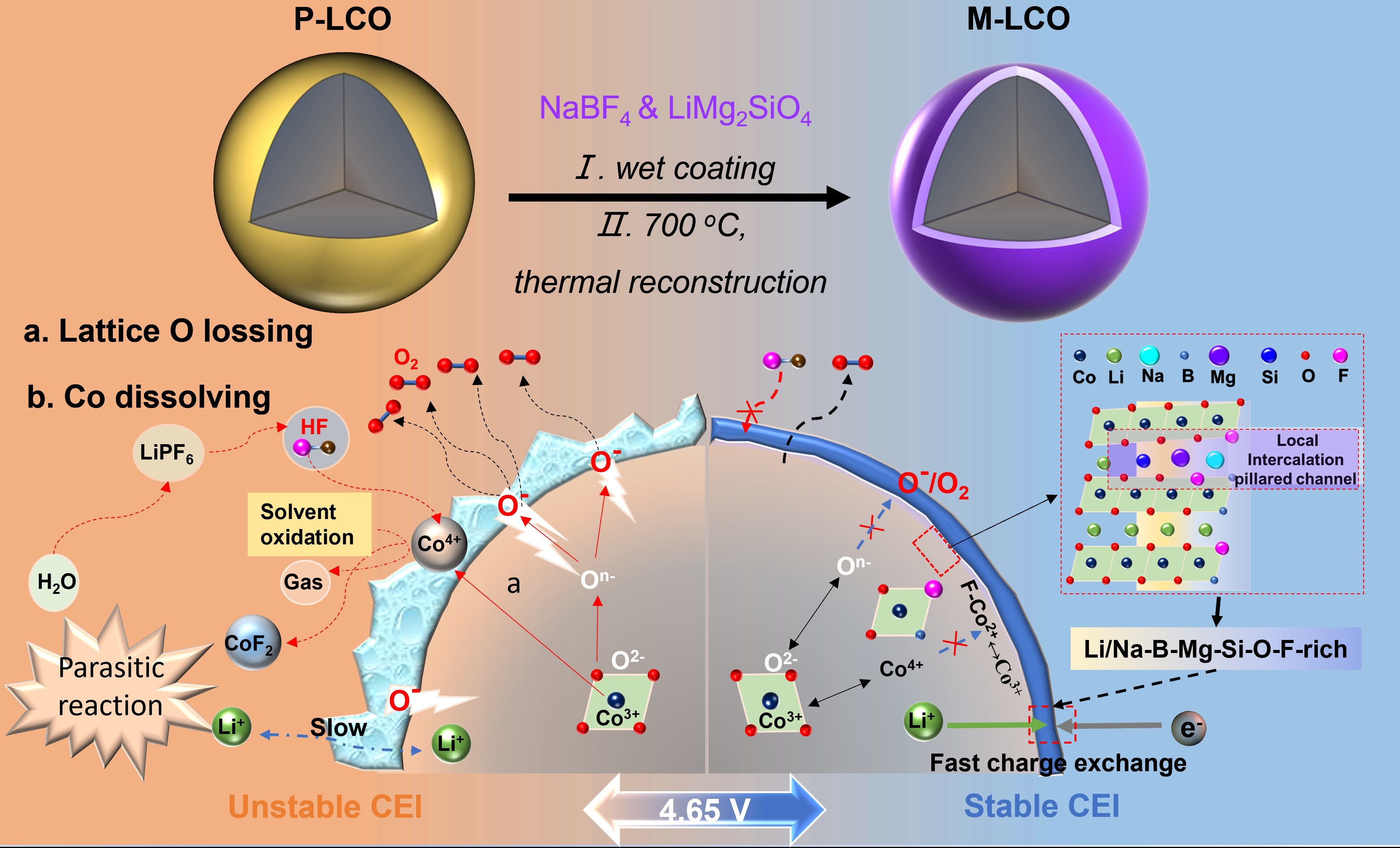
High-voltage and fast-charging LiCoO2 (LCO) is key to high-energy/power-density Li-ion batteries. However, unstable surface structure and unfavorable electronic/ionic conductivity severely hinder its high-voltage fast-charging cyclability. Here, we construct a Li/Na-B-Mg-Si-O-F-rich mixed ion/electron interface network on the 4.65 V LCO electrode to enhance its rate capability and long-term cycling stability. Specifically, the resulting artificial hybrid conductive network enhances the reversible conversion of Co3+/4+/O2-/n- redox by the interfacial ion-electron cooperation and suppresses interface side reactions, inducing an ultrathin yet compact cathode electrolyte interphase. Simultaneously, the derived near-surface Na+/Mg2+/Si4+-pillared local intercalation structure extremely promotes the Li+ diffusion around the 4.55 V phase transition and greatly stabilizes the cathode interface. Finally, excellent 3C fast charging performance is demonstrated with 73.8% capacity retention over 1000 cycles. Our findings shed new insights to the fundamental mechanism of interfacial ion/electron synergy in stabilizing and enhancing fast-charging cathode materials.
